Introduction
The Presidential Election in the USA is one of the most significant political events globally, drawing attention not just from American citizens but from people around the world. The process is complex, with a blend of history, tradition, and modern-day political dynamics that together shape the outcome of who will lead the United States for the next four years. This article delves deep into the intricate details of the Presidential Election in the USA, from its historical evolution to the upcoming 2024 election, providing a comprehensive guide for anyone looking to understand this critical democratic process.
 |
| Presidential Election in USA |
History of Presidential Elections
The history of presidential elections in the USA dates back to the late 18th century. Since the adoption of the Constitution in 1789, the nation has consistently held presidential elections, establishing a democratic tradition that has influenced many other countries. Initially, the process was less structured, with early elections often decided by a smaller, more elite group of electors. Over time, reforms and changes have made the process more inclusive and representative of the American populace.
Eligibility Criteria
To run for the office of President of the United States, a candidate must meet specific eligibility criteria. These requirements ensure that candidates have a sufficient connection to the country and a basic level of maturity and experience. The main criteria are:
- Natural-born Citizen: The candidate must be a natural-born citizen of the United States.
- Age Requirement: The candidate must be at least 35 years old.
- Residency Requirement: The candidate must have been a resident of the United States for at least 14 years.
These criteria must be met by Inauguration Day, ensuring that candidates have the necessary qualifications to assume the presidency.
 |
| Presidential Election in USA |
The Election Process
The process of electing a president in the USA is divided into several stages, each playing a critical role in determining the final outcome. The key stages include:
- Primary Elections and Caucuses
- National Conventions
- Election Campaigns
- General Election
- The Electoral College
Primary Elections and Caucuses
The primary elections and caucuses are the first steps in the presidential election process. These events determine the candidates who will represent each political party in the general election. Primaries and caucuses are held in different states, often starting more than a year before the general election.
Differences Between Primaries and Caucuses
Primary elections are state-level elections where party members vote for their preferred candidate. There are several types of primaries, including closed, semi-closed, open, and semi-open primaries. In contrast, caucuses are local meetings where party members discuss and vote on candidates. Both methods aim to gauge the support for each candidate within the party.
Importance of Early Primaries
Early primaries, such as those in Iowa and New Hampshire, are crucial because they can shape the momentum of a candidate’s campaign. Success in these states often attracts media attention, increases fundraising, and boosts the candidate’s chances in subsequent primaries.
Key States in the Primary Process
Certain states play a more significant role in the primary process due to their timing and political influence. States like California, Texas, and Florida have a large number of delegates and can significantly impact the outcome of the primary elections.
National Conventions
National conventions are held after the primary elections and caucuses. Each major political party holds a convention to formally nominate their presidential candidate. These conventions also serve as a platform to unify the party, set the campaign agenda, and rally supporters.
The Role of National Conventions
During the national conventions, delegates from each state cast their votes for the party’s presidential nominee. The candidate who secures the majority of delegate votes becomes the party’s official nominee. Additionally, the party’s vice-presidential candidate is typically chosen and announced during the convention.
Selection of Vice Presidential Candidates
The selection of the vice-presidential candidate, often called the running mate, is a strategic decision. The chosen candidate can balance the ticket, appeal to different voter demographics, and provide additional expertise or experience.
Election Campaigns
Once the presidential and vice-presidential candidates are chosen, the election campaign begins in earnest. Campaigns are extensive and multifaceted, involving travel, speeches, debates, advertisements, and endorsements.
Strategies Used in Campaigns
Candidates employ various strategies to connect with voters and gain their support. These strategies include grassroots campaigning, leveraging social media, hosting town hall meetings, and participating in televised debates.
The Role of Media
The media plays a significant role in election campaigns, shaping public perception and influencing voter opinions. News outlets, social media platforms, and political advertisements all contribute to the dissemination of information about candidates and their platforms.
Debates and Public Appearances
Debates and public appearances are critical components of the election campaign. They provide candidates with opportunities to articulate their policies, challenge their opponents, and directly engage with voters.
General Election
The general election is the culmination of the presidential election process. It is held on the first Tuesday after the first Monday in November every four years.
How General Elections Work
In the general election, voters across the country cast their ballots for their preferred presidential candidate. Although voters are technically selecting electors who will vote in the Electoral College, the outcome of the popular vote in each state generally determines which electors will cast their votes for the presidential candidates.
Popular Vote vs Electoral Vote
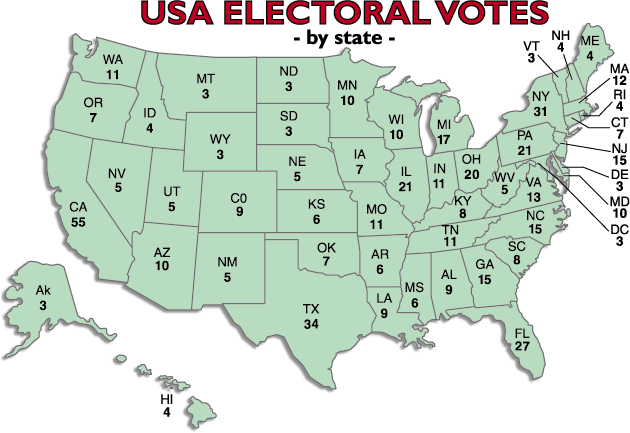
The general election includes both the popular vote and the electoral vote. While the popular vote reflects the choice of the electorate, the electoral vote ultimately decides the winner. Each state’s number of electoral votes equals its total number of Senators and Representatives in Congress.
The Electoral College
The Electoral College is a unique feature of the American presidential election process. It consists of 538 electors, with a majority of 270 electoral votes required to win the presidency.
Composition and Functioning of the Electoral College
Electors are chosen by political parties in each state. These electors meet in their respective state capitals in December following the general election to cast their votes for President and Vice President. The candidate who receives a majority of electoral votes (270 or more) wins the election.
Criticisms and Support
The Electoral College has been subject to both criticism and support. Critics argue that it can result in a candidate winning the presidency without securing the popular vote, as seen in the 2000 and 2016 elections. Supporters contend that it balances the influence of smaller states against larger ones.
Notable Instances of Electoral College Outcomes
Historical instances where the Electoral College has played a decisive role include the elections of 1876, 1888, 2000, and 2016. These elections highlighted the potential for discrepancies between the popular vote and the electoral vote.
Key Terms and Concepts
Several key terms and concepts are essential to understanding the presidential election process:
Super PACs
Super PACs are independent political committees that can raise and spend unlimited amounts of money to support or oppose candidates. They play a significant role in election campaigns, often funding advertisements and other campaign activities.
Swing States
Swing states, also known as battleground states, are states where the outcome of the election is uncertain. These states receive significant attention from candidates because they can swing the election in favor of either party.
Super Tuesday
Super Tuesday is a pivotal day in the primary election season when multiple states hold their primaries and caucuses. It often serves as a turning point in the race for the presidential nomination.
Impact of the 2024 Election
The 2024 presidential election is expected to have a profound impact on various aspects of American society, including domestic policies, international relations, and economic conditions.
Predictions and Potential Outcomes
Political analysts and experts predict that the 2024 election will be highly competitive, with key issues such as healthcare, immigration, and climate change taking center stage. The election's outcome will shape the future direction of the country.
Key Issues and Debates
Key issues likely to dominate the 2024 election include economic recovery post-pandemic, social justice, and foreign policy. Candidates’ positions on these issues will significantly influence voter preferences.
Comparison with Other Democracies
The US presidential election process differs from election processes in other democracies. While some similarities exist, notable differences highlight the unique aspects of the American system.
Differences in Election Processes
Unlike parliamentary systems where the head of government is chosen by the legislature, the US system involves a direct vote by the electorate, mediated through the Electoral College.
Similarities and Influences
The US election process has influenced other democracies, particularly in terms of campaign strategies and the use of technology in elections.
Role of Technology
Technology has increasingly influenced presidential elections, from social media campaigns to cybersecurity measures.
Influence of Social Media
Social media platforms play a crucial role in modern campaigns, allowing candidates to reach voters directly and engage with them in real-time.
Cybersecurity Concerns
Cybersecurity has become a significant concern, with efforts to safeguard the election process from interference and ensure the integrity of the vote.
Voting Technologies
Advancements in voting technologies aim to make the process more efficient and secure. However, they also raise concerns about accessibility and potential vulnerabilities.
Voter Participation
Voter participation is a critical aspect of the democratic process, with efforts continually made to increase turnout and ensure fair access to voting.
Trends in Voter Turnout
Historical trends in voter turnout reveal fluctuations based on factors such as political climate, campaign engagement, and voter enthusiasm.
Efforts to Increase Participation
Various initiatives aim to increase voter participation, including voter education programs, easier registration processes, and expanded voting options like mail-in ballots.
Voter ID Laws and Controversies
Voter ID laws remain a contentious issue, with debates over their impact on voter suppression versus their role in preventing election fraud.
Future of Presidential Elections
The future of presidential elections may see significant changes, driven by demographic shifts, technological advancements, and potential reforms.
Potential Reforms
Potential reforms include changes to the Electoral College, the implementation of ranked-choice voting, and adjustments to campaign finance regulations.
Impact of Demographic Changes
Demographic changes, such as shifts in population and voter preferences, will continue to influence election outcomes and campaign strategies.
Evolution of Political Campaigns
Political campaigns will likely evolve with changing technologies and voter expectations, incorporating more digital engagement and data-driven strategies.
Case Studies
Examining previous elections provides valuable insights into the dynamics of presidential elections and lessons for future campaigns.
Analysis of Previous Elections
Case studies of past elections, such as those in 2000 and 2016, highlight the complexities of the electoral process and the factors that can influence outcomes.
Lessons from Historical Elections
Historical elections offer lessons on campaign strategies, voter behavior, and the importance of key issues, informing current and future political campaigns.
FAQs
- What are the main steps in the presidential election process?
- How does the Electoral College work?
- What is the role of primary elections and caucuses?
- How are presidential candidates chosen in the USA?
- What is the significance of swing states in presidential elections?
- How can a candidate win the popular vote but lose the Electoral College?
Conclusion
The Presidential Election in the USA is a multifaceted process that reflects the country’s democratic values and political complexities. Understanding the various stages, from eligibility and primaries to the general election and the Electoral College, is essential for grasping how the American electoral system functions. As the 2024 election approaches, it will undoubtedly be a pivotal moment, shaping the future direction of the nation.
Suggestions for Further Reading
- "The American Political System" by Ken Kollman
- "Presidential Elections: Strategies and Structures of American Politics" by Nelson W. Polsby and Aaron Wildavsky
- Articles from "The Atlantic" and "Politico" on recent election trends and analyses
Inbound Links
- History of US Elections
- The Role of National Conventions
- Understanding the Electoral College
Outbound Links
- Official US Government Page on Presidential Elections
- Federal Election Commission Resources
- Articles on Voting Technologies and Cybersecurity from Leading Tech Journals